Tetsumi Kudo
Curated in collaboration with Joshua Mack.In cooperation with Hiroko Kudo and the estate of the artist.
June 20 – August 15, 2008
Main Gallery
For me, art is to doubt everything completely.
- Tetsumi Kudo
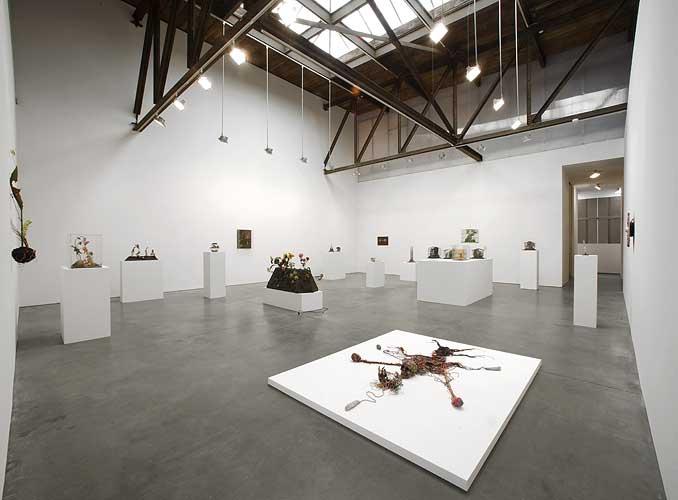
Andrea Rosen Gallery is delighted to announce the very timely first United States gallery exhibition of Tetsumi Kudo (1935 - 1990). This exhibition has been planned in conjunction with Kudo's major retrospective at the Walker Art Center opening October 15, 2008 and will continue our commitment to featuring influential historical artists who are under recognized in the United States.
At once raw and highly aesthetic, visceral and political, Kudo's sculpture is a significant precursor to much at the core of contemporary aesthetics. His use of alternative materials and detritus and his commitment to performances presage the physicality evident in work as diverse as the Chapman Brothers, David Altmejd and Paul McCarthy. Indeed, McCarthy included Kudo in Low Life Slow Life, an exhibition at the CCA Wattis Institute for Contemporary Arts, which explored influences critical to the development of his understanding of art making. Mike Kelley, who learned of Kudo in 1980, is writing for the catalog of the Walker Art Center's retrospective.
Over a thirty year career, Kudo, who worked in France and Japan, developed an extremely complex body of sculpture, installation, and performance-based work in reaction both to World War II and Japan's subsequent transformation into an industrial society and to European Humanism which, he believed, abetted environmental degradation and social malaise. Satirical, critical, yet matter of fact and at times poignant, his work draws both on Japanese tradition and Western Modernism, fusing the two in ways which are a model for the cultural transformations now attributed to younger artists in an age of globalization.
As for many Japanese artists of his generation, Kudo's intellectual outlook was formed by experiences of destruction and deprivation endured during the War and by the subsequent rise of mass consumerism on the ruins of a tradition-minded order. His works of the late 50s and early 60s, realized before he left Japan for Paris, are often fashioned from baskets accreted with small knots or from lengths of rope obsessively twisted around metal armatures. Titled with variations on the phrase "chain reaction," they reference the bombing of Hiroshima but also suggest that Kudo was seeking an energy that would generate a new society and a new art.
In reaction to the renewal of the United States Japan Security Treaty in 1960 -- an agreement which essentially maintained Japan's status as an occupied nation -- against nationwide protest, Kudo created Philosophy of Impotence, 1961, an installation comprised of hanging phalluses sculpted from black tape and tipped with spent flash bulbs. Representative of a nation awash in used junk, unable to resist the United States, and deformed by war and occupation, the piece was intended both as a provocation and as a reflection on man's lack of agency in modern society. During this time, Kudo exhibited and was affiliated with the Anti-Art and Neo-Dada movements which had supplanted Gutai as the most conceptually innovative force in Japanese visual culture.
Kudo was equally critical of Western Humanism, a reaction which became evident in his work once he and his wife, Hiroko, settled in Paris in 1963, where he became associated with the artists like Erro, Arman, Spoerri, and traveled in an intellectual circle which included Jean Jacques Lebel and Pierre Restany. To Kudo, the fundamental opposition of man and nature, life and death, and creation and destruction implicit in European philosophy was false. Reflecting Japanese culture, particularly Shintoism, he believed that these "poles" were instead aspects of a continuum. Our failure to understand our world holistically was the root cause of colonialism, racism, and environmental degradation resulting from an uncritical embrace of technology and industry.
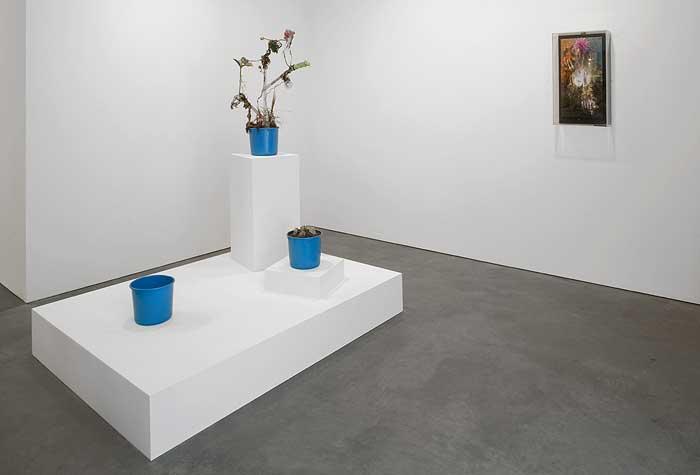
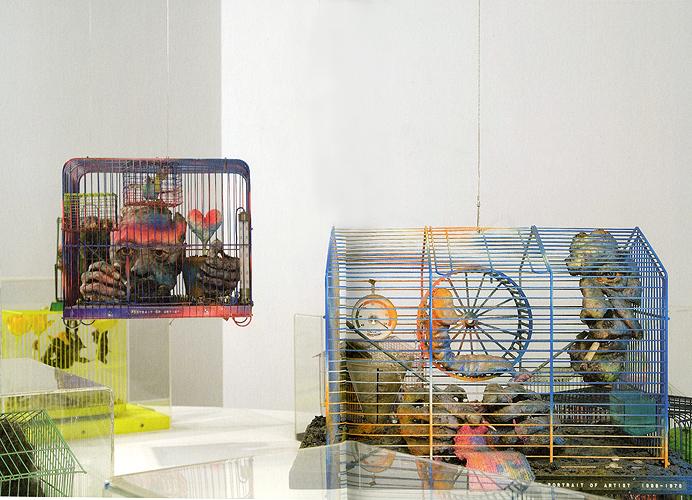
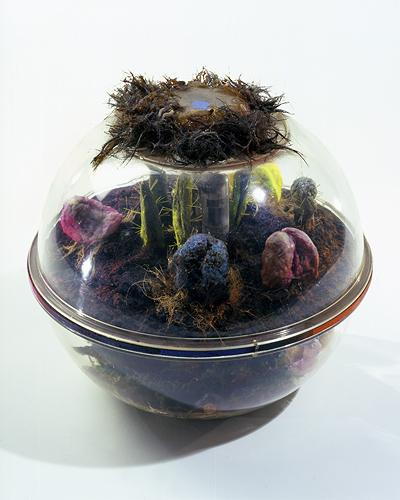
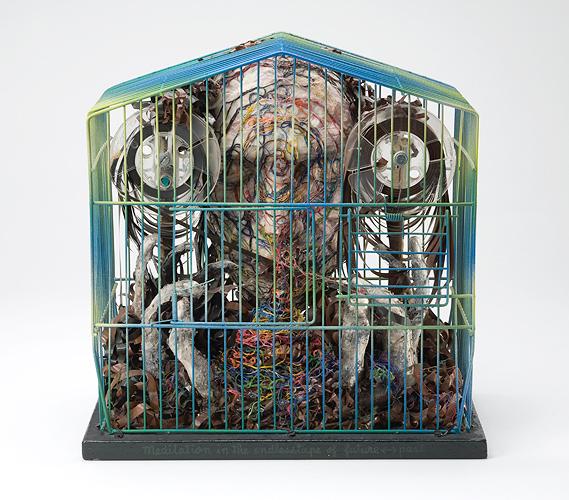
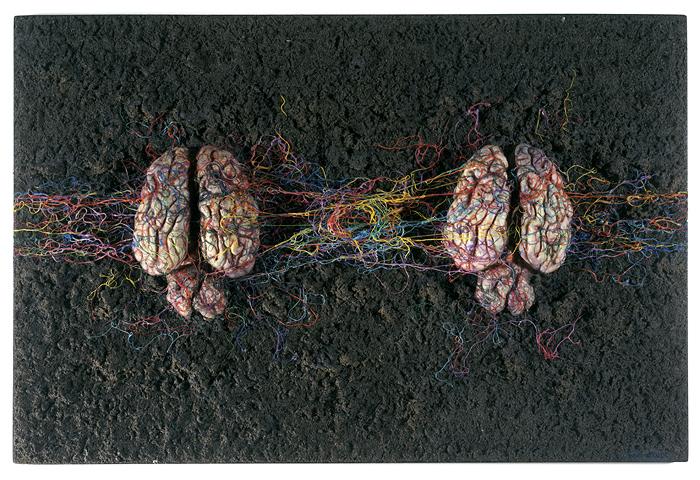
In response, he began to create cages in which body parts meld with transistors and circuit boards sprout plastic flowers; boxes in which disembodied eyes stare at magazine pages and ears listen to radios; and greenhouses in which electronics, plants, and body parts are grafted to each other. Many pieces glow in the dark. These are not social criticisms per se, but systematic analyses: representations of the artist's understanding of ours as a world in which nature, humanity, and technology controlled and nurtured each other in a closed circuit.
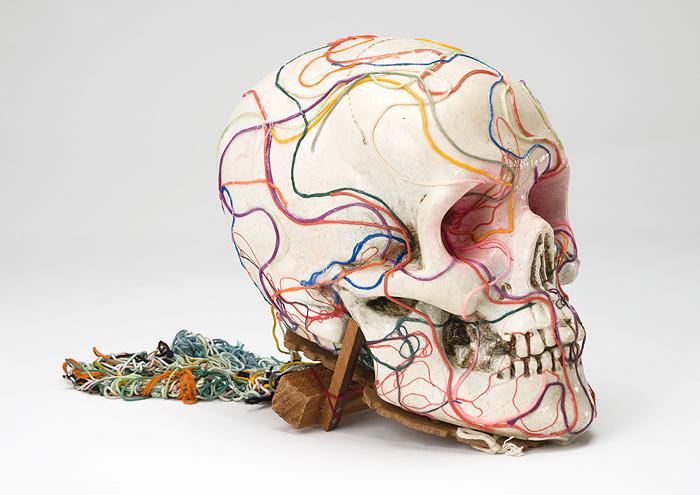
In the late 1970s during a period of ill health, Kudo began including lengths of colored string and reams of magnetic tape in his works to suggest the energy of thoughts, memory, and life moving within and between the mind, the body, and the animate world. By 1981, he had ceased using figurative elements, instead affixing yarn and thread to papier mache-like cylinders and cones. Kudo referred to these as trou noir and also suggested that several reflected the balance of centrifugal and centripetal forces which he believed unified Japan, not in social terms, but in a pantheistic sense. Although visual departures from his work of the 60s and 70s then, these pieces are mediations on the unity of opposites, the continuity of existence an d the structure of society. As such they synthesize anew the concerns implicit in all his work.
This exhibition will include approximately twenty-four works, incorporating each of these periods and dating from 1965 to 1988.
Of note, the Walker Art Center will publish a full length catalogue in conjunction with their exhibition with essays by Doryun Chong, Mike Kelley, and others.
Tetsumi Kudo was born in 1935 in Osaka, Japan and graduated from the Tokyo National University of Fine Arts in 1958. In 1957, he began exhibiting his work at the Salon of Independents, Yomiuri and had his first solo exhibition at the Galerie Blanche, Tokyo. He was awarded the Grand Prize and a travel grant to Paris through his participation in the 1962 Second International Young Artists Exhibition in Tokyo. His work made international appearances at the Venice Bienniale (1976), and the Biennial Sao Paulo (1977, awarded a special mention) while also appearing frequently in museums and galleries throughout Japan and France, with a growing recognition in Holland. Notable museum solo exhibitions include the National Museum of Art, Osaka (1994), a joint-exhibition and catalogue organized by the Van Reekum Museum and the Stedelijk Museum in Amsterdam (1991), as well as the Hirosaki City Museum, Aomori (1986). In the year before his death, Galerie du Génie and FIAC dedicated a retrospective and catalogue to Kudo's work. His work was most recently in a solo exhibition organized by La Maison Rouge and the Fondation Antoine de Galbert in Paris, accompanied by a catalogue written by Anne Tronche. His work can also be found in the collections of the Musée Moderne de la Ville de Paris, the Fonds National d'Art Contemporain, the Centre Georges Pompidou, and the National Museum of Art, Osaka. Kudo's work made a rare appearance to US audiences in the Guggenheim's 1994 exhibition, "Japanese Art After 1945: Scream Against the Sky," and again in 1998 with its inclusion in a group exhibition at the LA MoCA "Out of Action: Between performance and the Object, 1949-1979." Tetsumi Kudo died of cancer on November 12, 1990.
Text written by Joshua Mack.
For more information and images please contact Jeremy Lawson at j.lawson@rosengallery.com or 212.627.6000